 |
POPSICLE- a software suite to determine population structure and Ancestral Determinants of Phenotypes using Whole Genome Sequencing data |  |
MAIN INDEX ANALYTICAL PIPELINE CONTACT SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS POPSICLE Package Download Manual pages in HTML format Used Case |
 |
The advent of new sequencing
technologies has provided access to genome-wide markers which may be evaluated for
their association with the observed phenotypes. Recent studies have leveraged
these technologies and sequenced hundreds and sometimes thousands of strains to
improve accuracy of genotype-phenotype predictions. Sequencing of thousands of
strains is not practical for many research groups which argues for formulation
of new strategies that improve predictability using a fraction of cost and by
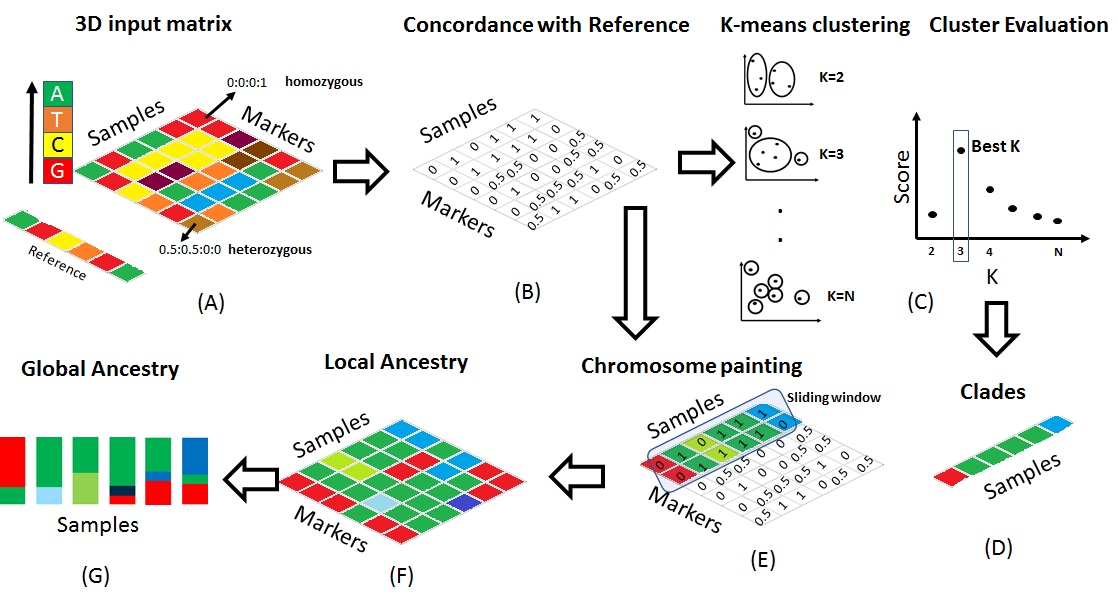
using only a few samples. We introduce here a novel computational algorithm
called POPSICLE that exploits the local genetic variations to infer blocks of
shared ancestries to construct complex evolutionary relationships. These
evolutionary relationships are subsequently visualized using chromosome
painting, as admixtures and as clades to acquire general as well as specific
ancestral relationships within populations. In addition, POPSICLE evaluates the
ancestral blocks for their association with phenotypes thereby bridging two
powerful methodologies from population genetics and genome-wide association
studies. In comparison to the existing tools, POPSICLE offers substantial
improvements in terms of accuracy, speed and automation. We evaluated
POPSICLE’s ability to find genetic determinants of P. falciparum’s resistance to Artemisinin using 57 out of 1,612 strains that were used in the
original study. POPSICLE was able to accurately infer key genes implicated in
the original study and found new gene families that were previously implicated
in resistance to Artemisinin. We further extended this analysis to find shared
ancestries among closely related P.
falciparum, P. reichenowi and P. gaboni species from Laverania subgenus of Plasmodium. POPSICLE
was able to accurately infer the population structure of Laverania subgenus and detected strains
which are coinfections involving P.
falciparum and P. gaboni. |
| CITATION: Jahangheer S. Shaik, Asis Khan and Michael E. Grigg, "POPSICLE: A Software Suite to Study Population Structure and Ancestral Determinants of Phenotypes using Whole genome Sequencing Data", submitted to PLoS special edition |